Serverless computing continues to evolve as one of the most powerful and scalable solutions in cloud-native application development. In 2025, serverless architectures are not just about “no servers”—they’re about smarter resource allocation, faster deployment, and reduced operational overhead.
However, with this innovation come hidden pitfalls that many businesses overlook. In this blog, we’ll explore best practices to leverage serverless architecture effectively and highlight the common traps to avoid in 2025.
What Is Serverless Architecture?
Before diving into the nuances, let’s define serverless architecture. Contrary to its name, serverless does involve servers—however, the responsibility for provisioning and managing these servers shifts from the user to the cloud provider. Popular platforms like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions exemplify this model.
Key Features:
- Auto-scaling and pay-as-you-go model
- Event-driven execution
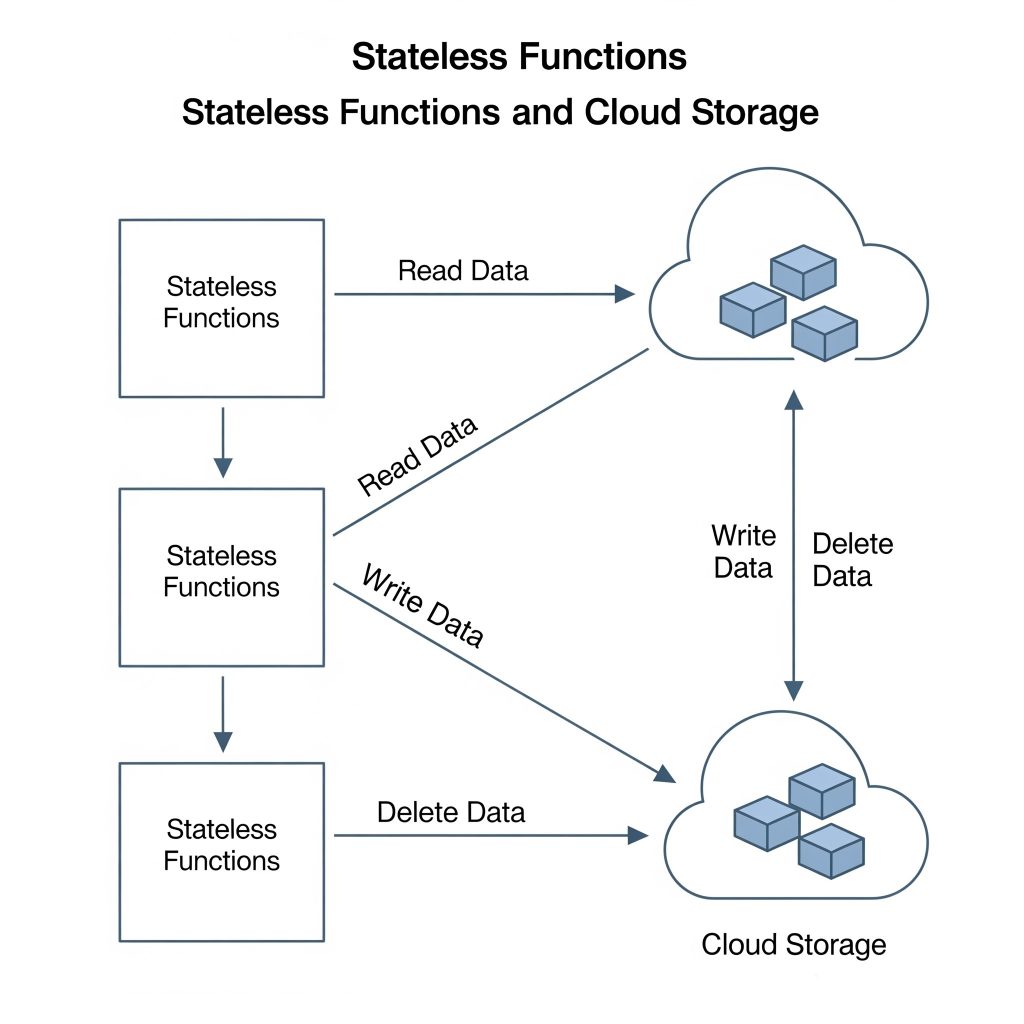
- Stateless backend processes
- Minimal infrastructure management
Best Practices for Serverless Architectures in 2025
1. Design for Statelessness
Each function call should be independent. Ensure your application components do not rely on shared in-memory state. Instead, use cloud-native storage like Amazon S3 or Firebase for state persistence.
2. Monitor Cold Starts
Cold starts, especially in languages like Java or .NET, can introduce latency. Opt for lightweight runtimes such as Node.js or Python and consider provisioning concurrency where available.
3. Use the Principle of Least Privilege
Restrict IAM roles and function access to only what’s necessary. This minimizes the attack surface and enforces better security standards.
➡️ Vital Role of Cybersecurity in Web Application Development
4. Modularize Your Functions
Avoid writing monolithic functions. Instead, break logic into smaller, reusable components. This improves testability and fault isolation.
5. Enable Observability
Integrate logging, tracing, and metrics from the outset. Use tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Datadog to gain visibility into function performance.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
1. Over-Triggering Events
Multiple triggers from sources like API Gateway, SNS, or SQS can lead to redundant executions and unnecessary costs. Carefully map out your trigger logic.
2. Vendor Lock-In
Serverless platforms often use proprietary services, making migration complex. To mitigate this, use frameworks like the Serverless Framework or Kubernetes-based alternatives like Knative.
3. Inadequate Timeout Configurations
Default timeout settings may not suit all workloads. Long-running processes should be handled asynchronously or split into smaller tasks.
4. Ignoring Local Development
Local development and testing can be cumbersome. Use tools like LocalStack or SAM CLI to simulate serverless environments offline.
5. Underestimating Costs
While serverless seems cost-effective, poorly optimized functions or high call volumes can inflate bills. Always analyze usage patterns and set budget alerts.
Serverless Use Cases to Watch in 2025
- Real-time file processing (e.g., image or video conversion)
- Chatbots and AI model triggers using cloud functions
- API backends for mobile or web apps
- Scheduled tasks (e.g., cron jobs)
Tools That Complement Serverless Architectures
Development Tools
- Serverless Framework
- AWS SAM
- Azure Durable Functions
Monitoring & Logging
- AWS CloudWatch
- Google Cloud Trace
- Datadog
Deployment & CI/CD
- GitHub Actions
- Jenkins with serverless plugins
- Bitbucket Pipelines
Final Thoughts
Serverless architectures in 2025 are maturing rapidly, offering unparalleled scalability and developer agility. Yet, to harness their full potential, organizations must adopt a strategic mindset—balancing innovation with control, flexibility with governance, and performance with observability.
By following best practices and staying aware of the potential pitfalls, you can deploy robust, cost-efficient, and scalable serverless systems that thrive in the dynamic cloud ecosystem.

